Start with an image on the worktable.
Click Histogram in the ribbon, and then click the Adjust tool in the palette to display the Histogram Adjustment dialog.
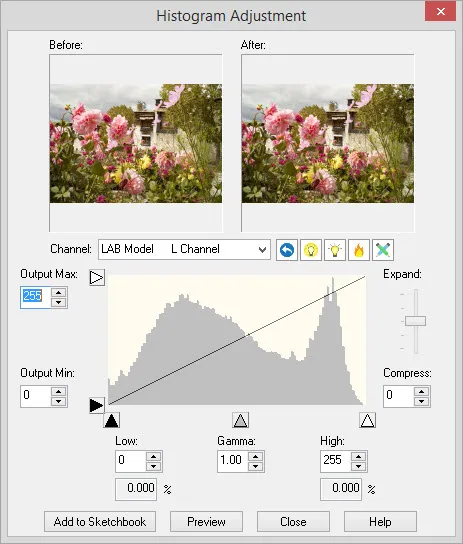
The histogram adjustment dialog lets you change the brightness and contrast of the image. Changes can be made by typing new values, clicking the arrow buttons, or by dragging the triangle-shape controls or slider along the edges of the histogram graph.
The graph will display the histogram for the current image in gray. The left end of the graph represents black and the right end of the graph represents white.
- If the gray graph does not reach the lower left corner, then the darkest pixels in the image are not completely black.
- If the gray graph does not reach the lower right corner, then the lightest pixels in the image are not completely white.
As the controls in the dialog are used to change the image, the new histogram reflecting the adjustments will appear in red.
Channel
The most common color model is RGB where the triplet refers to red, green and blue. A color defined by these values represents a point in a three-dimensional color space. Other color models have been developed to correlate with human perception. These models are all different ways of dividing the color space. These models all have luminance as one of the triplet parameters.
- LAB Model: The L stands for luminance. A controls the magenta to green spectrum and B controls the yellow to blue spectrum.
- YUV Model: The Y stands for luminance. U and V represent the color information in terms of red (U) and blue (V).
- YIQ Model: The Y stands for luminance. I stands for in-phase and indicates a range from orange to blue. Q stands for quadrature and indicates a range from purple to green.
Preset Buttons
- Reset to default: Use to restore all the values to the original settings.
- Glow: Use to increase the contrast between light and dark in the image.
- Lighten: Use to lighten the darkest pixels of the image.
- Warm: Use to lighten overall by converting many in the range of lighter pixels to the same value.
- Pastel: Use to apply extreme lightening to the darkest pixels of the image.
Adjusting Brightness
- Output Max: To darken the lightest pixels in the image, drag the Max control (white triangle on the top left edge of histogram) down.
- Output Min: To lighten the darkest pixels in the image, drag the Min control (black triangle on the lower left edge of histogram) up.
Adjusting Contrast
- Low: As you drag the Low control (black triangle on the bottom left edge) to the right, all pixels values to the left of the control get converted to the level of the control. This has the effect of making the image darker since many pixels of various values all get converted to the same value. The color that the pixels convert to is black if the Output Min control is set to zero, otherwise the color is the value of the Output Min control. If there is a gap before the gray histogram begins to rise, then no pixels are affected until the control reaches the beginning of the gray graph.
Percentage readout: The percentage value below the Low control displays the percentage of pixels that are between zero and the low value. Contrast for these pixels will be lost since they get converted to the same value.
- High: As you drag the High control (white triangle on the bottom right edge) to the left, all pixels values to the right of the control get converted to the level of the control. This has the effect of making the image lighter since many pixels of various values all get converted to the same value. The color that the pixels convert to is white if the Output Max control is set to 255, otherwise the color is the value of the Output Min control. If there is a gap before the gray histogram reaches the right edge of the graph, then no pixels are affected until the control reaches the beginning of the gray graph.
Percentage readout: The percentage value below the High control displays the percentage of pixels that are between 255 and the high value. Contrast for these pixels will be lost since they get converted to the same value.
- Gamma: The Gamma control adjusts midtone brightness. This control helps prevent from pushing some parts of the image into becoming over-exposed or under-exposed. White will still be white. Black will still be black, and everything between will just be pushed upwards or downwards but not out of range. The range for this control is 0.2 to 5.0.
- Expand/Compress: The slider along the right edge of the histogram will adjust the midtones of the image. Drag the slider up to expand. You will notice that the red histogram will spread out and expand, adding more extreme lights and darks to the image. In other words, the darks get darker and the lights get lighter. Drag the slider down to compress. This will create a peak in the red histogram in the middle of the graph resulting in more gray-looking image.

 Electric Quilt 8
Electric Quilt 8